the apprehension and relocation test for shoulder labral tear|jobes relocation test : purchasing This test is often used following a positive Apprehension Test to confirm the presence of anterior shoulder instability or impingement. A positive Jobe Relocation Test indicates possible diagnoses such as glenohumeral instability, subluxation, dislocation , or impingement. See more Resultado da 1 de abr. de 2022 · 34. Entenda como calculamos a reputação. Está com problemas com Gimi Medicina Diagnóstica? Reclamar. Publicidade. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da No contexto do Ensino Fundamental, as características da avaliação diagnóstica incluem ser formativa, diversificada e orientada para a compreensão. Ela é formativa no sentido de que não visa atribuir notas, mas sim fornecer informações valiosas sobre o progresso do aluno. A .
This test is often used following a positive Apprehension Test to confirm the presence of anterior shoulder instability or impingement. A positive Jobe Relocation Test indicates possible diagnoses such as glenohumeral instability, subluxation, dislocation , or impingement. See more
Apprehension test. The patient is supine and the examiner applies a downward force on the wrist while stabilizing the elbow to evaluate [3] for anterior shoulder laxity. [4] Evidence. Test .Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and .
Apprehension and Relocation Test For this test it's preferable that the patient lies supine on the examination table. Then the examiner flexes the elbow at 90° and abducts the shoulder to 90° as well.In the normal shoulder, static and dynamic stabilizers help keep the humeral head centered in the glenoid fossa, allowing movement in the glenohumeral joint through a large range of .
The relocation test is performed immediately after a positive result on the anterior apprehension test. With the patient supine, the examiner applies posterior force on the proximal humerus.Apprehension is a better criterion than pain for a positive apprehension or relocation test. The anterior drawer test (when pain does not prevent it from being performed) is helpful for .The apprehension, relocation, and release tests can all be done in quick succession with the patient supine. The apprehension test is performed with the patient’s arm at 90° of abduction, . Anterior Apprehension Test. The anterior apprehension test is performed by lying the patient supine on the examination table. The examiner positions the shoulder to 90 .
The main tests for anterior instability include the apprehension test, relocation test and surprise test. The apprehension test is carried out by flexing the patients elbow to 90°, then .
By combining both apprehension and relocation tests, . The passive compression test: a new clinical test for superior labral tears of the shoulder. Am J Sports Med 2007; 35: 1489–94. [Google Scholar] 26. Berg EE, Ciullo JV. A clinical test for superior glenoid labral or ‘SLAP' lesions. Other tests used for identifying SLAP tears include the biceps load tests, crank test, and dynamic labral shear test. To perform the biceps load test I, the patient is positioned supine with their shoulder at 90°, elbow at 90°, and forearm supinated. The examiner then performs the apprehension test.The patient may have a positive apprehension test, relocation test, and/or anterior release test . Murrel, GAC. An assessment of the interexaminar reliability of tests for shoulder instability. The journal of Shoulder and Elbow .
Multidirectional shoulder instability (MDI) is a condition characterized by generalized instability of the shoulder in at least 2 planes of motion (anterior, posterior, or inferior) due to capsular redundancy. . Bankart lesion is anteroinferior labral tear. Kim lesion is posteroinferior labral avulsion. MDI is also referred to as AMBRI. A .
Pertinent elements in history taking to best elucidate the nature of a potential SLAP tear (or other associated shoulder injuries) include: Acute onset of “deep” shoulder pain. . Anterior Apprehension Test. . Jobe Relocation. The Jobe relocation test is utilized with the previous apprehensive testing maneuver. Once the patient reports a .Positive Finding: The test is considered positive if the patient demonstrates apprehension with external rotation of the shoulder. Shoulder pain is not an indicator of a positive apprehension test and may suggest impingement. If the patient demonstrates apprehension, proceed to the Jobes relocation test for further confirmation. A posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex, and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes. Diagnosis can be made clinically with positive posterior labral provocative tests and confirmed with MRI studies of the shoulder.SLAPprehension Test. Jo Gibson. This test was described by Berg and Ciullo in 1998 and was developed after 2 patients described cervical spine and shoulder pain and a click associated with turning a steering wheel Le. horizontal flexion and internal rotation after RTA. Arthroscopy revealed the presence of a type II SLAP lesion in both patients.. Test. The patient is examined .
The Crank Test is commonly used in orthopedic examinations to test for integrity of the glenoid labrum; it tests for a labral tear. This test is quite similar in many ways to the McMurray Test for meniscal damage in the knee.. The Glenoid Labrum ryanmcjohnson Involved Structures. glenoid labrum; ligaments of glenohumeral jointConclusion: Based on pooled data, the diagnostic accuracy of the Neer test for impingement, the Hawkins−Kennedy test for impingement and the Speed test for labral pathology is limited. There is a great need for large, prospective, well-designed studies that examine the diagnostic accuracy of the numerous physical examination tests of the . In van Kampen et al’s study of six of these clinical tests (apprehension, relocation, release, anterior drawer, load and shift, and hyperabduction tests) for traumatic anterior shoulder instability, the relocation test was the most sensitive (96.7%), the anterior drawer test was the most specific (92.7%), and the release test showed the best .
transverse bending testing machine
The test is performed on patients with shoulder pain and a history of chronic anterior shoulder dislocation in order to determine shoulder instability and possibly the presence of a labral tear . Jerk Test For Shoulder Labrum Tear. Jerk Test For Shoulder Labrum Tear. A positive Jerk Test is indicative of a potential posterior-inferior labral tear or lesion or posterior-inferior instability of the shoulder complex. Stabilize the patient’s scapula with one hand and hold the affected arm at 90° abduction and internal rotationSpecial tests for shoulder instability. The Apprehension Test, Jobe's Relocation Test, Composite SLAP Tear Test-item Cluster, Jobe's Relocation Test (Apprehension Tests), Biceps Load 2, Obrien's Active, Compression Test, Posterior Inferior Labral Lesion, Jerk Test, Speed's Test, Yergason's Test, Compression Rotation Test, Kim's Test. The reliability, specificity, .In addition, the apprehension, Jobe relocation, and release tests all demonstrated high specificity for anterior instability, with the apprehension test having the greatest positive likelihood ratio at 17.2. 17. The load and shift test is a test for both anterior and posterior shoulder instability.
A low-bias study revealed that the negative predictive value can be improved by the addition of the relocation test, which is performed by repeating the apprehension test with the examiner’s hand pressing down on the anterior .Results: The results of the O'Brien test (63% sensitive, 73% specific) and Jobe relocation test (44% sensitive, 87% specific) were statistically correlated with presence of a tear in the labrum and the apprehension test approached statistical significance. Performing all 3 tests and accepting a positive result for any of them increased the .DOI: 10.1177/0095399703258690 Corpus ID: 12180540; An Evaluation of the Apprehension, Relocation, and Surprise Tests for Anterior Shoulder Instability @article{Lo2004AnEO, title={An Evaluation of the Apprehension, Relocation, and Surprise Tests for Anterior Shoulder Instability}, author={Ian K.Y. Lo and Blake Nonweiler and Michael R. Woolfrey and Robert B .
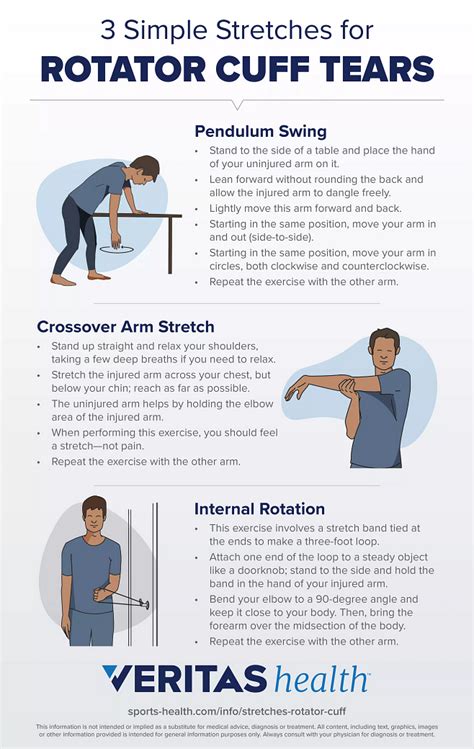
- Internal lag test for rotator cuff tear - External lag test for rotator cuff tear - Neer test for shoulder impingement - Hawkins Kennedy test for shoulder impingement - Scapular repositioning test - Scapular assistance test - Sulcus sign - Apprehension relocation tests - Load and shift test for glenohumeral instability; RELATED TOPICSPurpose [edit | edit source]. This test is used to assess the stability of the Glenohumeral joint.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patient should be seated. The therapist stabilizes the scapula to the thorax with one hand, while the other hand is placed across the posterior GH joint line and humeral head, and the web space across the patient's acromion. . The index finger should the . - Dynamic Relocation Test - Dynamic Rotatory Stability Test - Bony Apprehension Test - identical to the standard apprehension test except that the arm is brought to only 45 of abduction and 45 of external rotation. A positive result should alert the examiner to the possibility of a bony lesion as the cause of symptomatic shoulder instability.
Learn how to diagnose Labral Tear Cluster with this helpful video. It covers the basics of how to perform the Shoulder Special Test Cluster, as well as recognizing and interpreting test results. . (Apprehension, Surprise and Jobe's Relocation Tests) . Compression Rotation Test. Biceps Load 2 - Shoulder Special/Orthopedic Test for Superior .Apprehension and Relocation Test For this test it's preferable that the patient lies supine on the examination table. Then the examiner flexes the elbow at 90° and abducts the shoulder to 90° as well. . Labral Tears (SLAP lesions) Shoulder Exam. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the margins of the glenoid fossa. It .Anterior apprehension test and relocation test. . as they usually coexist with other shoulder problems such as impingement or labral tears . In young athletes, as mentioned before, laxity should not be mistaken for instability. . Hannafin J.A., Altchek D.W., Warren R.F. An evaluation of the shoulder relocation test. Am. J. Sports Med. 1994 .- Dynamic Relocation Test - Dynamic Rotatory Stability Test - Bony Apprehension Test - identical to the standard apprehension test except that the arm is brought to only 45 of abduction and 45 of external rotation. A positive result should alert the examiner to the possibility of a bony lesion as the cause of symptomatic shoulder instability.
A multitude of physical examination tests for diagnosing anterior shoulder instability have been described4,8-10, with the apprehension test and the relocation test being the most com-mon6,7. In addition, the anterior drawer test, recognized as a measure of shoulder laxity, can be used as a provocative maneu-ver for anterior shoulder . The apprehension and relocation test is specific for examining anterior shoulder instability. [16] For patients with a history of stroke, if they present with concomitant subluxation and shoulder pain, the physical examination for the rotator cuff tendinopathy, acromioclavicular arthropathy, and subacromial impingement helps identify the cause .
shoulder strengthening after exam
Resultado da Tweets with replies by Mia K. (@miakhalifa) / Twitter. We’ve detected that JavaScript is disabled in this browser.
the apprehension and relocation test for shoulder labral tear|jobes relocation test